D-CUBED COMPONENTS
D-Cubed 3D DCM
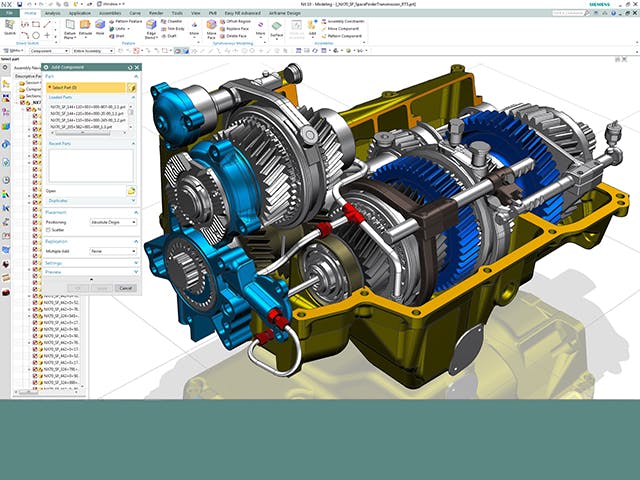
Solve assembly constraints, simulate kinematics and sketch in 3D with 3D Dimensional Constraint Manager (DCM)—the most widely adopted 3D geometric constraint solver for CAD/CAM/CAE applications.
Why D-Cubed 3D DCM?
Develop custom applications in part and assembly modeling with D-Cubed 3D Dimensional Constraint Manager (DCM) for reduced risk and time-to-market. D-Cubed 3D DCM is a geometric constraint solver that increases design and engineering productivity in the following areas:
- Part-positioning in assembly modeling, using dimensions and assembly constraints
- Kinematic simulation of constrained assemblies and mechanisms
- Controlling the shape of parts without relying on a design history—sometimes known as direct editing or direct modeling
- Configuring 3D sketches in support of 3D features, 3D pipe/wire routes
See what's included
3D Geometric constraint solving
Solve 3D geometric constraints applied to a wide range of entities, including points, lines, planes, circles, ellipses, cylinders, tori and parametric curves/surfaces.
Dimensions and constraints include distance, angle, radius, parallel, perpendicular, tangent, concentric, symmetric, normal, midpoint and pattern. Variable dimensions can be linked by equations, for example, linking the rotation or translation of one component with another to enable kinematic simulation. Dimensions can be bounded to specify a range of values which a distance or angle dimension can assume when solving the model.
Constraining free-form geometry
Apply geometric constraints to position rigid bodies with respect to free forms curves and surfaces. Control the shape free-form curves with parameters including tangency, curvature and curve length.
Solving options and diagnostics
Select from various solving modes to obtain your preferred solutions, such as moving the minimum number of geometries, or moving geometries the minimum amount relative to each other.
Obtain comprehensive feedback about the status of the model, including what is well-defined, under-defined and over-defined.
Stay connected with PLM Components
Read the blog
Gain new perspectives on PLM Components and the PLM market in general.