增材制造技术与工艺
增材制造可以使用各种技术完成,例如粘结剂喷射和层压物体制造,但以下技术是最常用于 3D 打印的技术。
材料挤出(FDM、FFF)
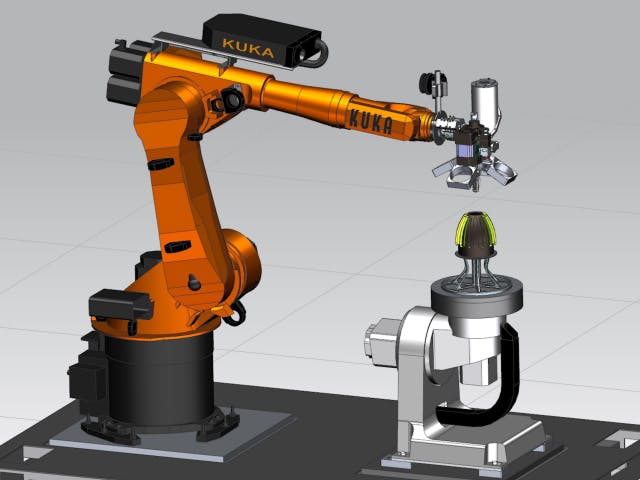
该工艺使用线轴材料(通常基于聚合物)和加热的沉积头。头部熔化灯丝以长流挤出材料。FDM 是大多数低成本桌面打印机中使用的技术,因为零件价格实惠,并且以线轴形式提供现成的材料。多轴FDM软件由西门子和我们的合作伙伴在我们的 NX 解决方案中率先推出。我们的解决方案经过了几代人的测试和改进,是适合这些类型操作的强大平台。
立体光刻 (SLA)
立体光刻是最古老的增材制造 (AM) 工艺之一,它使用液态树脂来创建 3D 对象。在大多数情况下,树脂是用紫外线固化的。SLA 打印机与其他技术有些不同,因为零件是按 –Z 方向打印的。这意味着一旦凝固,打印部件的每一层都会被向下推入树脂中,而不是像大多数其他工艺那样向上构建。
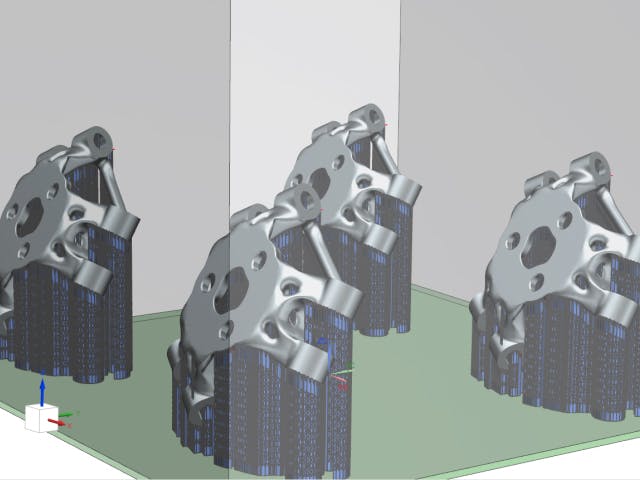
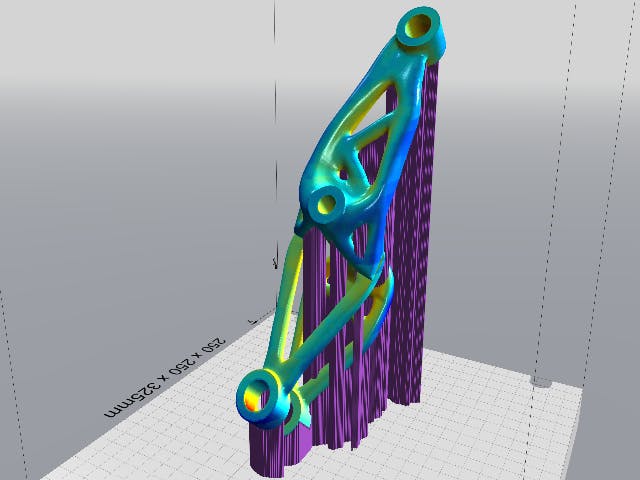
粉末床熔融(DMLS、SLS、EBM)
粉末床熔融是一个描述许多增材制造工艺的术语,包括金属增材制造。所有这些都涉及粉末材料床,该材料以平面方式逐层熔合。这是使用多种材料类型完成的,包括塑料和金属。多种技术用于熔断粉末材料。西门子 NX 的集成特性允许您执行必要的任务,例如在构建托盘中对零件进行 3D 嵌套或构建用于 PBF 打印的支撑结构,而无需数据转换或使用外部软件包。这样做的好处是,当您的零件几何形状通过修订而变化时,这些下游操作会自动更新,几乎不需要用户交互,从而节省了大量的设计和设置时间。
粘结剂喷射
粘结剂喷射是增材制造 (AM) 技术的一类,它使用喷墨式打印头选择性地将液体粘合剂沉积到粉末材料上,以形成固体 3D 对象。由于粉末分子通过粘合剂化学反应结合在一起,而不是通过施加的热能熔化或烧结,因此粘结剂喷射技术与粉末床熔融技术不同。
材料喷射
材料喷射是一种增材制造 (AM) 工艺,其中液态树脂液滴通过喷墨式打印头选择性沉积,并通过紫外线 (UV) 照射固化以构建坚固的 3D 对象。材料喷射被认为是增材制造中最精确的方法之一。材料喷射能够打印厚度小于 20 微米的层,以构建具有精细细节、高精度和光滑表面的 CAD 设计而闻名。