Transforming the everyday
Transforming industry together and turning ideas into innovation.
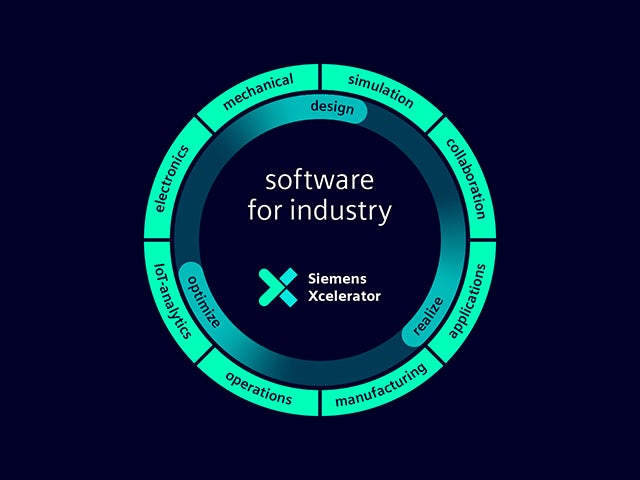
Comprehensive digital twin
Our digital twin is the single source of trust to enable smart decisions based on data. Only Siemens combines the real and digital worlds to build a true digital enterprise.
Sustainability
We create sustainable industrial innovation for a world we want to live in, today and tomorrow, and for an industry that desires to leave no trace on this planet.
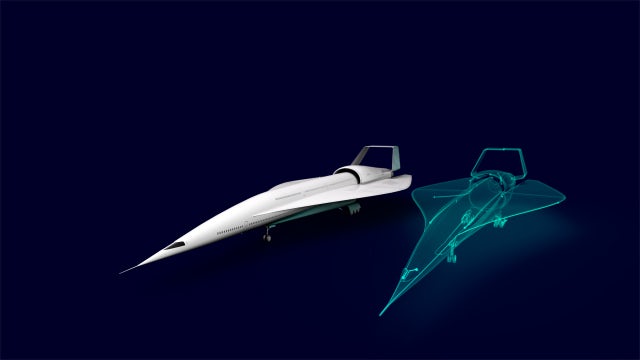
Future of mobility
We are enabling the future of mobility on air, land and sea by helping create a transportation revolution to make travel more enjoyable and sustainable.
Additive manufacturing
We deliver pragmatic additive manufacturing for all size companies. We enable end-to-end processes for additive manufacturing to make it easy, cost-effective and pervasive.
Artificial intelligence
By leveraging big data, our AI innovations and solutions enable smarter decision-making, greater efficiencies, improved quality, and faster time to market while unlocking new business.
Model based system design
Our integrated model-based system design (MBSE) methodology unifies all the domains needed to create today’s smart systems and are all focused on accelerating product innovation or business success.
What does it take to become a digital enterprise?
Surf Loch is using today’s digital technology to disrupt the surfing industry. With a small team of dedicated engineers, they used software and services within the Siemens Xcelerator portfolio to give all surfers an opportunity to ride the perfect wave whenever they want.
Learn more about their inspirational digital transformation journey.
Transforming the everyday
Visit our blog to find more information about the Siemens Xcelerator portfolio and Siemens Xcelerator as a Service.