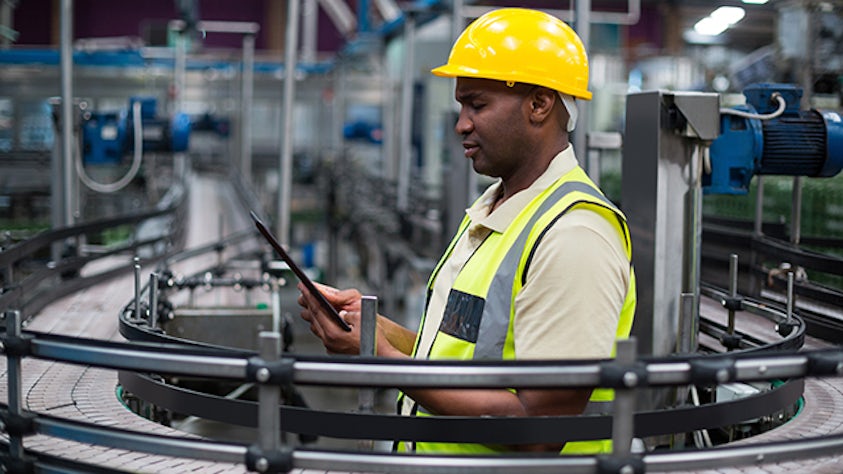
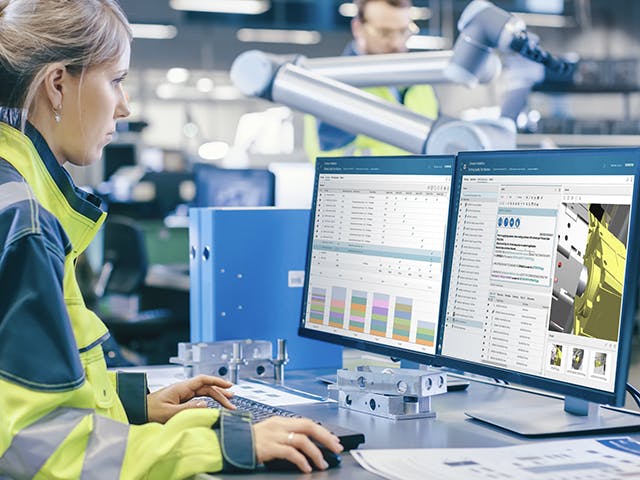
전자 작업 지침은 완전하고 시행 가능한 작업자 지침을 제공합니다. 전자 작업 지침 소프트웨어는 작업자가 지정된 대로 작업을 완료할 수 있도록 구성되어 있습니다. 전자 작업 지침은 특정 작업자와 취한 조치를 모두 추적합니다. 작업자 승인 또는 특정 데이터 수집을 요구하거나 제조 감사 추적에서 정보 기록을 생성하도록 작업을 구성할 수 있습니다. 작업자는 간단한 클릭, 특정 "예" 입력 또는 자세한 파라메트릭 데이터 수집을 통해 수행되는 각 작업을 인식합니다. 전자 작업 지침 소프트웨어는 작업을 완료하기 위해 전자 서명이 필요할 수도 있습니다.
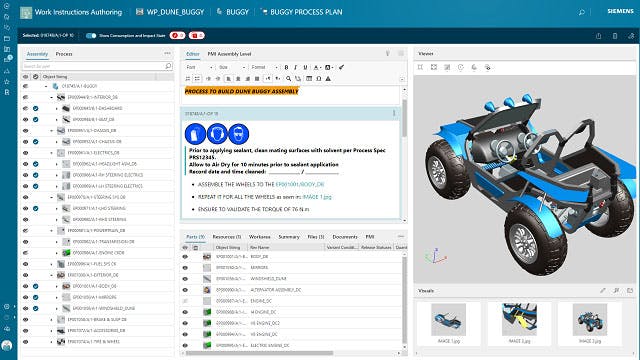
포괄적인 2D 및 3D 작업 지침 저작 및 보기 애플리케이션 제품군을 사용하면 3D 보기와 최신 프로세스 단계를 제공하여 작업 현장에 대한 조립 지침의 커뮤니케이션을 개선할 수 있습니다.
전자 작업 지침의 AR은 중요한 작업을 수행하기 위해 현장 인력에 의존하는 제조 작업의 품질과 생산성을 개선하는 데 이상적입니다. 여기에는 복잡하고 장기간의 조립 절차를 포함하는 고도로 구성 가능한 제품의 소량 생산과 조립 오류로 인해 높은 비용이 발생하는 조립이 포함됩니다.
전자 작업 지침 소프트웨어를 사용하면 작업 목록을 특정 순서 또는 임의의 순서로 실행하도록 구성할 수 있습니다. 재료가 다음 작업으로 이동되기 전에 모든 필수 작업을 성공적으로 완료해야 합니다. 전자 작업 지침 소프트웨어는 데이터 수집 시 모니터링되는 상한 및 하한으로 데이터 수집과 관련된 작업을 구성할 수 있습니다.
전자 작업 지침 소프트웨어는 다음과 같은 기능을 수행합니다.
- 작업자를 안내합니다.
- 절차 시행
- 라인 정리 의무화
- 데이터 수집 및 값 확인
- 예외에 대한 조치를 취합니다.
- 전자 서명 통합
- 감사 내역을 채웁니다.
제조 계획에서 엔지니어는 BOP(Bill of Process)에 따라 작업에 대한 전자 작업 지침을 작성할 수 있습니다. 제조 프로세스 계획 소프트웨어는 텍스트 지침을 참조 부품, 리소스 및 3D 그래픽 표현을 포함한 시각 보조 도구에 연결하여 작업 현장 직원에게 정확하고 명확한 지침을 제공합니다.
작업자 입력의 경우 전자 작업 지침이 작업 정의에서 양식을 자동으로 생성하고 작업자가 각 값을 입력합니다. 입력하거나 스캔하면 각 값이 상한 및 하한에 대해 확인되며 사양을 벗어난 값으로 인해 작업이 실패합니다.
사양을 벗어난 상태 또는 기타 프로세스 실패가 구성된 비즈니스 규칙에 따라 제품을 보류하거나, 재작업 또는 MRB(Material Review Board)로 라우팅하거나, 메시지를 이메일로 보내는 등의 작업을 자동으로 시작하도록 전자 작업 지침을 구성할 수 있습니다.
효과적인 전자 작업 지침 소프트웨어는 다양한 제조 절차를 정확하게 모델링할 수 있도록 완전히 구성할 수 있습니다. 작업 목록은 전자 절차를 통해 작업 셀, 워크스테이션 또는 리소스(장비)에 할당될 수 있습니다. 전자 작업 지침 소프트웨어가 모듈형인 경우 작업 및 작업 목록을 한 번 정의하여 여러 절차에서 사용할 수 있습니다. 작업 목록에 대한 변경 사항은 작업 목록의 모든 발생에 자동으로 적용됩니다.
전자 작업 지침의 작업은 제조 공정이 변경됨에 따라 쉽게 수정할 수 있습니다. 전자 작업 지침 소프트웨어는 작업자가 올바른 지침 수정본을 사용할 수 있도록 개정 관리 기능으로 설계되었습니다.
라인 클리어런스는 전자 절차에 의해 쉽게 시행됩니다. "공정 시작" 및 "공정 종료" 작업은 하나의 단위, 로트 또는 배치만 작업 셀에서 공정하도록 합니다.