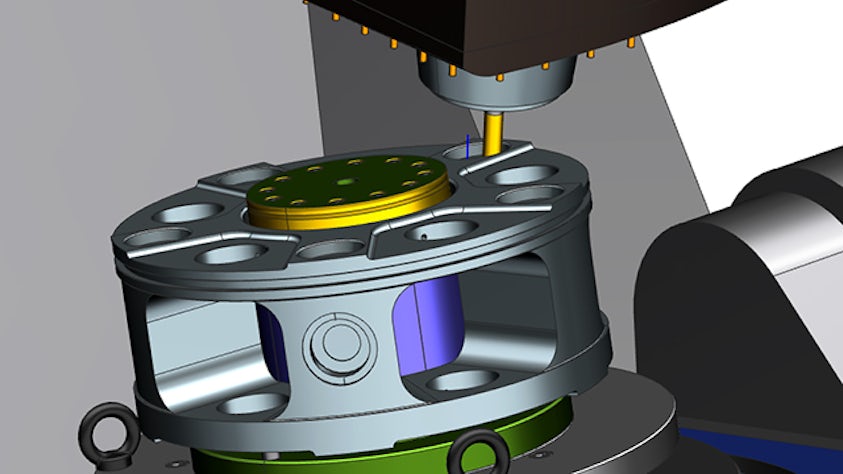
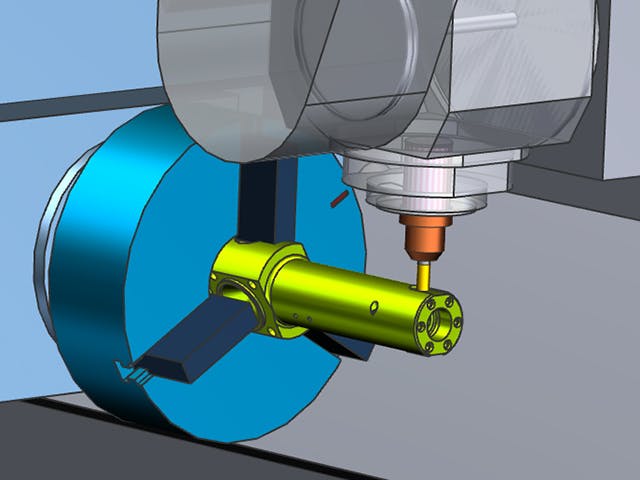
Computer-aided manufacturing plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing, accelerating operations and delivering components with unmatched precision and consistency. It is designed to optimize efficiency, minimize material wastage, and reduce energy consumption, aligning with the industry's growing focus on sustainability. By seamlessly integrating advanced technologies such as Computer-aided design (CAD), Product Lifecycle management (PLM), and Manufacturing execution system (MES), CAM empowers manufacturers to streamline their operations, helping to streamline workflows and enhance collaboration between departments. This enables them to bring products to market faster while maintaining the highest standards of quality.
Choosing the best computer-aided manufacturing solution
Finding the right computer-aided manufacturing solution can be challenging, given the diverse range of applications it needs to support. To help navigate this decision, consider the following key factors:
CAD-CAM Compatibility: Evaluate the software's capacity to seamlessly import CAD files without data loss using data translators, connecting your entire design and manufacturing process through a single platform. This enables quick and easy file importation by directly communicating the models and assemblies from the CAD component.
Programming Automation: Look for CAM software offering fully automated CNC feature recognition to streamline programming tasks and reduce manual programming.
Ease of Use: Opt for CAM software that prioritizes user-friendliness in machining operations. Look for features that facilitate easy job setups, swift machining operations, and quick generation of toolpaths. A user-friendly interface enhances efficiency and reduces the learning curve for operators.