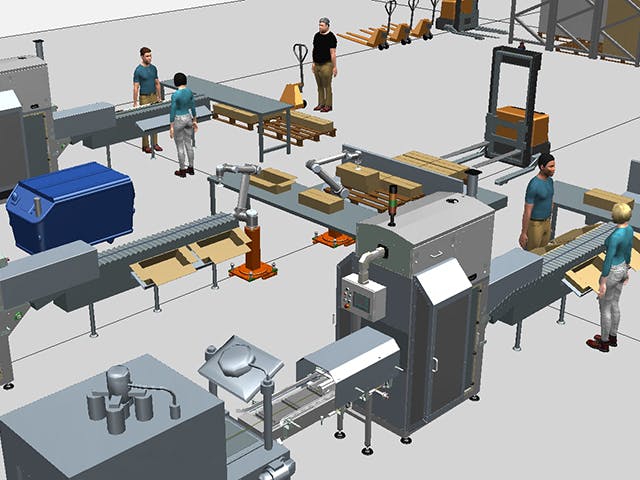
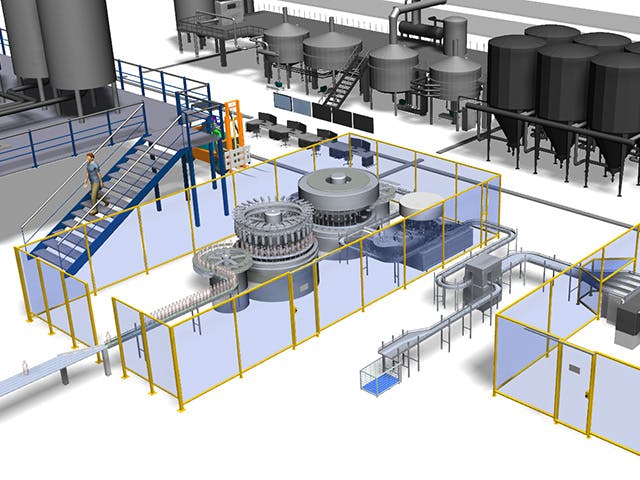
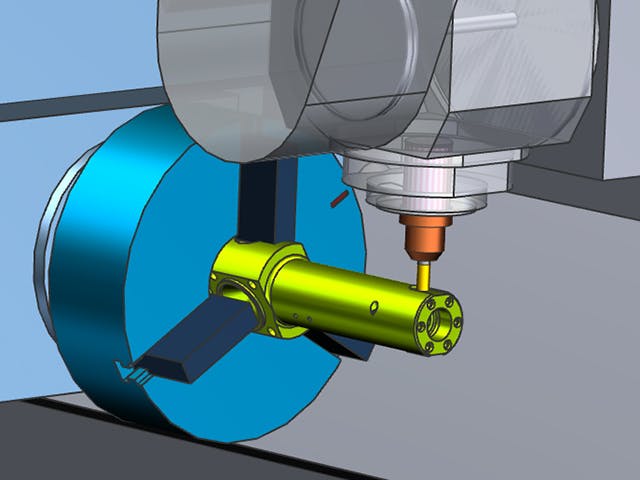
Digital manufacturing is the use of an integrated, computer-based system comprised of simulation, 3D visualization, analytics and collaboration tools to create product and manufacturing process definitions simultaneously. Digital manufacturing evolved from manufacturing initiatives such as design for manufacturability (DFM), computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM), flexible manufacturing and lean manufacturing that highlight the need for collaborative product and process design.
Many of the long-term benefits of product lifecycle management (PLM) cannot be achieved without a comprehensive digital manufacturing strategy. Digital manufacturing is a key point of integration between PLM and shop floor applications and equipment, enabling the exchange of product-related information between design and manufacturing groups. This alignment allows manufacturing companies to achieve time-to-market and volume goals, as well as realize cost savings by reducing expensive downstream changes.
Related products: Tecnomatix | NX | Solid Edge