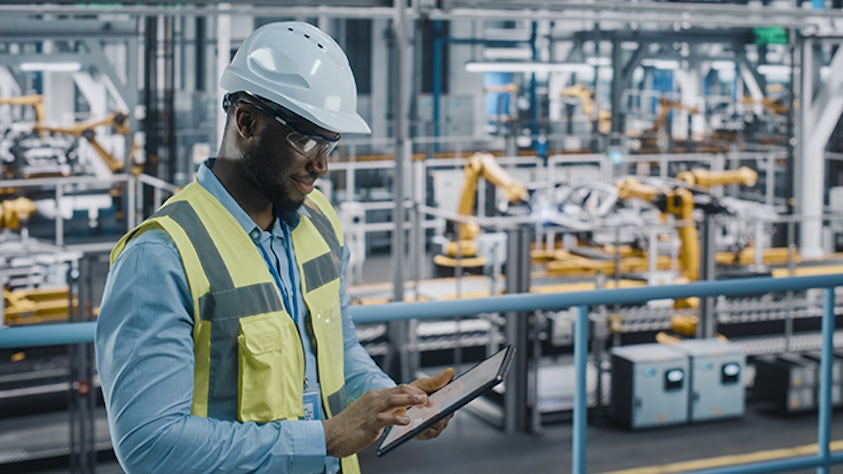
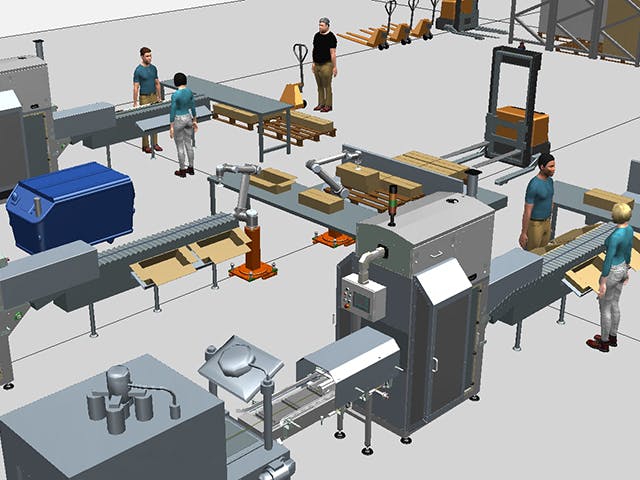
Digitální výroba je použití integrovaného počítačového systému složeného ze simulací, 3D vizualizace, analytiky a nástrojů pro spolupráci k současnému vytváření definic produktů a výrobních procesů. Digitální výroba se vyvinula z výrobních iniciativ, jako je design pro vyrobitelnost (DFM), počítačově integrovaná výroba (CIM), flexibilní výroba a štíhlá výroba, které zdůrazňují potřebu kolaborativního návrhu produktů a procesů.
Mnoha dlouhodobých výhod řízení životního cyklu výrobku (PLM) nelze dosáhnout bez komplexní strategie digitální výroby. Digitální výroba je klíčovým bodem integrace mezi PLM a dílenskými aplikacemi a zařízeními, což umožňuje výměnu informací souvisejících s produktem mezi konstrukčními a výrobními skupinami. Toto sladění umožňuje výrobním společnostem dosáhnout cílů v oblasti doby uvedení na trh a objemu a také dosáhnout úspor nákladů snížením nákladných následných změn.
Související produkty: Tecnomatix | NX | Solid Edge