Technologie a procesy aditivní výroby
Aditivní výrobu lze provádět pomocí různých technik, jako je Binder Jetting a Laminated Object Manufacturing, ale níže uvedené technologie se nejčastěji používají pro 3D tisk.
Vytlačování materiálu (FDM, FFF)
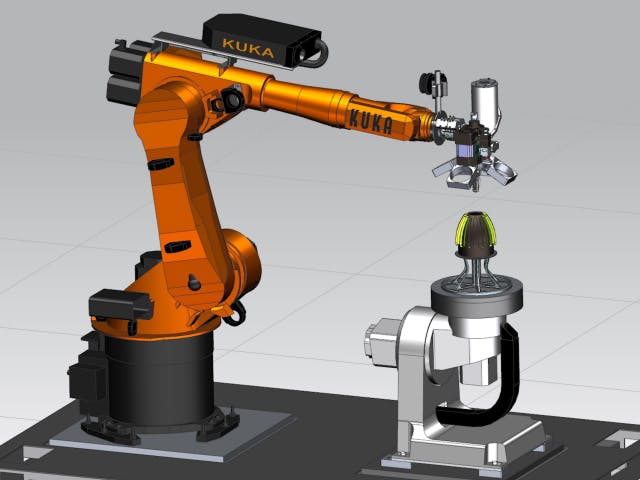
Tento proces využívá cívku materiálu (obvykle na bázi polymeru) a vyhřívanou nanášecí hlavu. Hlava taví vlákno a vytlačuje materiál v dlouhém proudu. FDM je technologie používaná ve většině levných stolních tiskáren kvůli cenové dostupnosti dílů a snadno dostupným materiálům ve formě filamentu/cívky. Software pro víceosé FDM byl průkopníkem společnosti Siemens a jejích partnerů v našich řešeních NX. Naše řešení bylo testováno a vylepšováno po několik generací a je nejrobustnější platformou pro tyto typy provozů.
Stereolitografie (SLA)
Stereolitografie je jedním z nejstarších procesů aditivní výroby (AM) a využívá tekuté pryskyřice k vytváření 3D objektů. Ve většině případů se pryskyřice vytvrzují pomocí ultrafialového světla. SLA tiskárny se poněkud liší od ostatních technologií, protože díl je tištěn ve směru –Z. To znamená, že po ztuhnutí je každá vrstva tištěného dílu tlačena dolů do pryskyřice, místo aby byla budována nahoru, jako je tomu u většiny ostatních procesů.
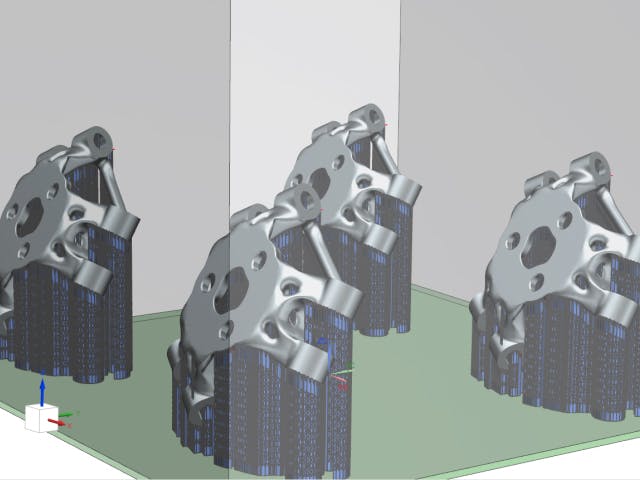
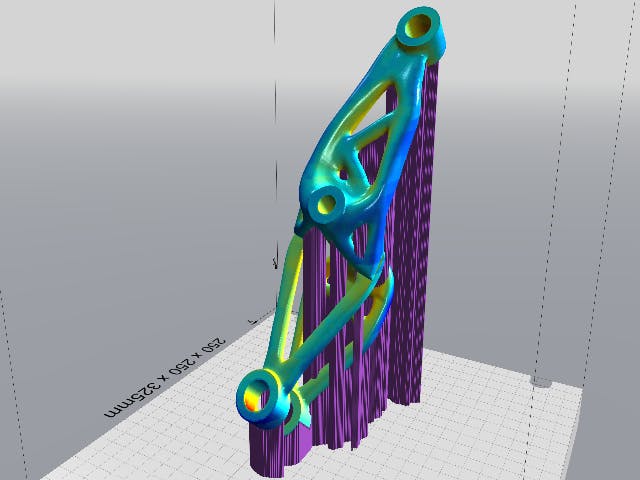
Powder Bed Fusion (DMLS, SLS, EBM)
Powder Bed Fusion je termín, který popisuje mnoho aditivních procesů, včetně aditivní výroby z kovů. Všechny zahrnují lože práškového materiálu, který se taví vrstvu po vrstvě planárním způsobem. To se provádí s více typy materiálů, plastem i kovem. K tavení práškového materiálu se používá celá řada technologií. Integrovaná povaha Siemens NX umožňuje provádět nezbytné úkoly, jako je 3D vnoření dílů do zásobníku nebo konstrukce podpůrných konstrukcí pro tisk PBF bez překladů dat nebo pomocí externích softwarových balíčků. Výhodou je, že když se geometrie dílu mění prostřednictvím revizí, tyto následné operace se automaticky aktualizují s malou interakcí uživatele, což šetří velké množství času na návrh a nastavení.
Pojivo tryskání
Binder Jetting je kategorie technik aditivní výroby (AM), které využívají tiskové hlavy ve stylu inkoustových tiskáren k selektivnímu nanášení tekutého pojiva na práškový materiál za účelem vytvoření pevných 3D objektů. Vzhledem k tomu, že molekuly prášku jsou spojeny dohromady adhezivní chemickou reakcí namísto tavení nebo slinování z aplikované tepelné energie, techniky tryskání pojiva se liší od technik fúze práškového lože.
Tryskání materiálu
Tryskání materiálu je proces aditivní výroby (AM), při kterém se kapičky tekuté pryskyřice selektivně nanášejí pomocí tiskových hlav ve stylu inkoustových tiskáren a tuhnou vystavením ultrafialovému (UV) světlu, aby se vytvořil pevný 3D objekt. Tryskání materiálu je považováno za jednu z nejpřesnějších metod aditivní výroby. Tryskání materiálu, které je schopné tisknout ve vrstvách o tloušťce menší než 20 mikronů, je známé pro vytváření CAD návrhů s jemnými detaily, vysokou přesností a hladkými povrchy.